Bravais lattice
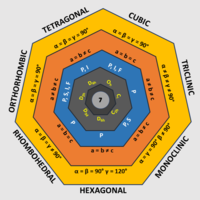
A bravais lattice is like a very organized way of arranging things. Imagine you have a bunch of toys and you want to put them all in a box. You could just throw them in randomly or you could put them in neat rows and columns so they fit perfectly, that's what a bravais lattice is like.
Now, imagine you have a bunch of atoms or molecules instead of toys. Scientists use bravais lattices to describe how these atoms or molecules are arranged in a solid, like a crystal. Each bravais lattice is made up of a repeating unit called a unit cell, which is like a small box that contains a certain number of atoms or molecules arranged in a specific way.
There are different types of bravais lattices, each with its own unique arrangement of atoms or molecules. Some types have atoms arranged in a cube-like structure, while others have them in a rectangular or hexagonal shape. Scientists use these lattices to understand how materials behave and interact with each other, which can help them develop new materials with specific properties like strength or conductivity.
So, a bravais lattice is a very organized way of arranging atoms or molecules in a crystal, similar to how you organize toys in a box. It helps scientists understand how materials behave and can lead to new discoveries and inventions.
Now, imagine you have a bunch of atoms or molecules instead of toys. Scientists use bravais lattices to describe how these atoms or molecules are arranged in a solid, like a crystal. Each bravais lattice is made up of a repeating unit called a unit cell, which is like a small box that contains a certain number of atoms or molecules arranged in a specific way.
There are different types of bravais lattices, each with its own unique arrangement of atoms or molecules. Some types have atoms arranged in a cube-like structure, while others have them in a rectangular or hexagonal shape. Scientists use these lattices to understand how materials behave and interact with each other, which can help them develop new materials with specific properties like strength or conductivity.
So, a bravais lattice is a very organized way of arranging atoms or molecules in a crystal, similar to how you organize toys in a box. It helps scientists understand how materials behave and can lead to new discoveries and inventions.
Related topics others have asked about:
