Bretton Woods System
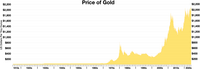
The Bretton Woods system was an agreement that was made after World War II in which countries around the world agreed to use the U.S. dollar as the main currency for international trade. The agreement was made because the U.S. dollar was a strong and stable currency, so it made sense for all countries to use it for these purposes. The agreement also set up rules for how countries would buy and sell currencies from each other, as well as how much gold each country would hold. This system allowed countries to buy and sell goods without worrying about their currency losing value, which was a major issue before the agreement.
Related topics others have asked about:
