Bridgman's thermodynamic equations
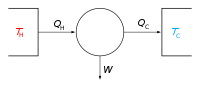
Bridgman’s thermodynamic equations are a way to understand how materials change when we change their temperature, pressure or volume.
Imagine you have a cup of water. If you heat the water up, it will start to boil and turn into steam. This is because heat makes the water’s molecules move faster and further apart.
Now let’s say you want to understand this process mathematically. You would use Bridgman’s thermodynamic equations to figure out how the temperature, pressure and volume of the water are affecting each other.
The equations are like a recipe that tells you how to mix different ingredients together. The ingredients in this case are temperature, pressure and volume. The recipe tells you how these ingredients are related to each other and how they change when you add heat or pressure.
Bridgman’s equations are complex and involve a lot of math, but at the most basic level they are telling us that when you change one of these factors (like temperature), the other factors will change as well (like pressure or volume).
So to understand how the water in our cup is changing, we need to use Bridgman’s equations to see how these factors (temperature, pressure, and volume) are all related to each other. Once we have this understanding, we can predict how the water will behave as we change these factors.
In summary, Bridgman’s thermodynamic equations help us understand how materials, like water in our example, change when we change the temperature, pressure or volume. They are like a recipe that tells us how different “ingredients” are related to each other and how they change when we add more or less of them.
Imagine you have a cup of water. If you heat the water up, it will start to boil and turn into steam. This is because heat makes the water’s molecules move faster and further apart.
Now let’s say you want to understand this process mathematically. You would use Bridgman’s thermodynamic equations to figure out how the temperature, pressure and volume of the water are affecting each other.
The equations are like a recipe that tells you how to mix different ingredients together. The ingredients in this case are temperature, pressure and volume. The recipe tells you how these ingredients are related to each other and how they change when you add heat or pressure.
Bridgman’s equations are complex and involve a lot of math, but at the most basic level they are telling us that when you change one of these factors (like temperature), the other factors will change as well (like pressure or volume).
So to understand how the water in our cup is changing, we need to use Bridgman’s equations to see how these factors (temperature, pressure, and volume) are all related to each other. Once we have this understanding, we can predict how the water will behave as we change these factors.
In summary, Bridgman’s thermodynamic equations help us understand how materials, like water in our example, change when we change the temperature, pressure or volume. They are like a recipe that tells us how different “ingredients” are related to each other and how they change when we add more or less of them.
Related topics others have asked about:
