Circle of antisimilitude
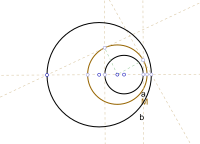
Okay kiddo, imagine you have two circles, one big and one small. Now, let's say you draw a line that goes through the centers of both circles. This line is called the "radical axis."
Now, let's draw two more lines that go through any point on each circle. These two lines will intersect at a new point. Let's call this point "P."
The circle of antisimilitude is a new circle that goes through point P and is perpendicular to the radical axis. This means that if we draw a line from point P to any point on the big circle, and then draw a line from that same point on the big circle to the intersection point of the two initial lines, the length of the first line will be equal to the length of the second line multiplied by a constant factor. This constant factor is known as the "power of P with respect to the circles."
Basically, the circle of antisimilitude is a special circle that helps us understand the relationship between two other circles and a point outside of them.
Now, let's draw two more lines that go through any point on each circle. These two lines will intersect at a new point. Let's call this point "P."
The circle of antisimilitude is a new circle that goes through point P and is perpendicular to the radical axis. This means that if we draw a line from point P to any point on the big circle, and then draw a line from that same point on the big circle to the intersection point of the two initial lines, the length of the first line will be equal to the length of the second line multiplied by a constant factor. This constant factor is known as the "power of P with respect to the circles."
Basically, the circle of antisimilitude is a special circle that helps us understand the relationship between two other circles and a point outside of them.
Related topics others have asked about:
