Cusp (singularity)
Imagine you have a ball and you want to balance it on top of a pointy cone-shaped object. The place where the ball touches the cone is called the cusp. The cusp is where the ball is perfectly balanced, but if it moves even a little bit in any direction, it will fall over.
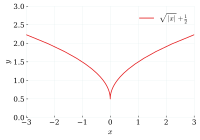
In math, a cusp is a point where a curve (like a line or a parabola) changes direction suddenly. It's like a sharp turn on a road. At the cusp, the curve is perfectly balanced, but it can't continue in the same way. It has to change direction.
A singularity is a special kind of cusp. In math, it's a point where something strange happens. For example, if you try to divide the number 1 by 0, you get a singularity. It's a point where the math doesn't work anymore. It's like trying to get to the top of a mountain, but finding out that the trail suddenly ends and you can't go any further.
In science, singularities are important because they can tell us about the nature of the universe. For example, black holes are thought to have singularities at their centers. They are points where the laws of physics break down and we don't fully understand what happens there.
So, a cusp is like the point where a ball balances on a cone, and a singularity is a special kind of cusp where crazy things happen.
In math, a cusp is a point where a curve (like a line or a parabola) changes direction suddenly. It's like a sharp turn on a road. At the cusp, the curve is perfectly balanced, but it can't continue in the same way. It has to change direction.
A singularity is a special kind of cusp. In math, it's a point where something strange happens. For example, if you try to divide the number 1 by 0, you get a singularity. It's a point where the math doesn't work anymore. It's like trying to get to the top of a mountain, but finding out that the trail suddenly ends and you can't go any further.
In science, singularities are important because they can tell us about the nature of the universe. For example, black holes are thought to have singularities at their centers. They are points where the laws of physics break down and we don't fully understand what happens there.
So, a cusp is like the point where a ball balances on a cone, and a singularity is a special kind of cusp where crazy things happen.
Related topics others have asked about:
