Defibrillation
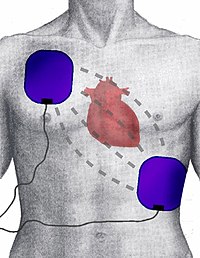
Defibrillation is the process of using a special machine called a defibrillator to help someone's heart beat again when it has stopped. Think of the heart like a machine that pumps blood throughout the body. Sometimes, the machine can stop working like when it runs out of batteries or gets tangled up in wires. Similarly, the heart can stop working for different reasons, like when someone has a heart attack or is in an accident.
When this happens, doctors use a defibrillator, which sends a small electric shock through the heart. It's like giving the heart a little jump-start to get it working again. The defibrillator can also help the heart go back to its normal rhythm if it's beating too fast or too slow.
To use a defibrillator, doctors will put special pads on the person's chest that connect to the machine. The machine will then analyze the person's heart rhythm and tell the doctors whether a shock is needed. If it is, the machine will give a small electric shock through the pads to the person's chest.
Defibrillation can save someone's life by restarting their heart and allowing blood to flow through their body again. It's important to call for emergency medical help right away if someone is not breathing or has no pulse, because defibrillation may be needed to bring them back to life.
When this happens, doctors use a defibrillator, which sends a small electric shock through the heart. It's like giving the heart a little jump-start to get it working again. The defibrillator can also help the heart go back to its normal rhythm if it's beating too fast or too slow.
To use a defibrillator, doctors will put special pads on the person's chest that connect to the machine. The machine will then analyze the person's heart rhythm and tell the doctors whether a shock is needed. If it is, the machine will give a small electric shock through the pads to the person's chest.
Defibrillation can save someone's life by restarting their heart and allowing blood to flow through their body again. It's important to call for emergency medical help right away if someone is not breathing or has no pulse, because defibrillation may be needed to bring them back to life.
Related topics others have asked about:
