Dielectric barrier discharge
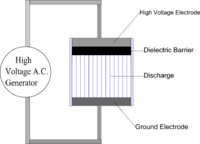
Dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) is a way of creating electricity by using two electrodes and a dielectric material between them. It works like this: the two electrodes are placed close together, and a dielectric material, like plastic or glass, is put between them. When a voltage is applied to the electrodes, it creates an electric field. This electric field causes the electrons in the dielectric material to move, creating a spark or discharge. This spark produces electricity, which can then be used to power electronic devices.
