Document Object Model
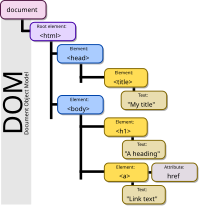
The Document Object Model (DOM) is like a map that helps your computer figure out how to show a webpage on your screen. It's like an instruction manual that tells it which pieces and colors to put together. It starts with a single root element (the main page), and then breaks all the other bits down into "nodes" that are arranged in a tree-like structure. Each node is an object that holds information like the text and images on a page, and the different parts of a website like the navigation, sidebar, and footer. When you open a web page, your browser reads the DOM and uses it to build the page as you see it.
Related topics others have asked about:
