DuPont analysis
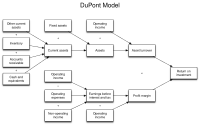
Do you want to know how a company makes money? Dupont analysis can help you understand that.
Let's say there is a company called ABC. ABC makes money by selling things like phones, clothes, or cars. But for a company to make money, it needs to do a lot of different things right. Dupont analysis helps us break down the process of making money into smaller parts.
Dupont analysis looks at three things:
1. Profit Margin: This tells us how much of the total revenue a company gets to keep as profit after it pays for expenses like salaries and materials. For example, if ABC earns $100 in revenue, but it spends $80 on salaries, rent, and materials, then its profit margin would be $20 or 20%.
2. Asset Turnover: This tells us how well a company uses its assets (its things like land, buildings, and equipment) to make money. For example, if ABC has $100 worth of assets and it earns $200 in revenue, then its asset turnover is 2 because it is generating $2 in revenue for every dollar of assets it has.
3. Financial Leverage: This tells us how much a company borrows to finance its assets. For example, if ABC has $100 worth of assets and it borrows $80 from a bank to buy those assets, then its financial leverage is 0.8 or 80%.
When we combine these three things, we get a formula that looks like this:
Dupont analysis:
Return on Equity (ROE) = Profit Margin x Asset Turnover x Financial Leverage
So if ABC has a profit margin of 20%, an asset turnover of 2, and a financial leverage of 80%, then its Return on Equity (ROE) would be 32%.
ROE tells us how much profit a company is making for every dollar that is invested in it. So if ABC had $100 worth of shares and earned an ROE of 32%, then it would make $32 in profit for every dollar that was invested in it.
In summary, Dupont analysis helps us understand how a company makes money by breaking down the process into smaller parts: profit margin, asset turnover, and financial leverage which ultimately helps us calculate the Return on Equity (ROE).
Let's say there is a company called ABC. ABC makes money by selling things like phones, clothes, or cars. But for a company to make money, it needs to do a lot of different things right. Dupont analysis helps us break down the process of making money into smaller parts.
Dupont analysis looks at three things:
1. Profit Margin: This tells us how much of the total revenue a company gets to keep as profit after it pays for expenses like salaries and materials. For example, if ABC earns $100 in revenue, but it spends $80 on salaries, rent, and materials, then its profit margin would be $20 or 20%.
2. Asset Turnover: This tells us how well a company uses its assets (its things like land, buildings, and equipment) to make money. For example, if ABC has $100 worth of assets and it earns $200 in revenue, then its asset turnover is 2 because it is generating $2 in revenue for every dollar of assets it has.
3. Financial Leverage: This tells us how much a company borrows to finance its assets. For example, if ABC has $100 worth of assets and it borrows $80 from a bank to buy those assets, then its financial leverage is 0.8 or 80%.
When we combine these three things, we get a formula that looks like this:
Dupont analysis:
Return on Equity (ROE) = Profit Margin x Asset Turnover x Financial Leverage
So if ABC has a profit margin of 20%, an asset turnover of 2, and a financial leverage of 80%, then its Return on Equity (ROE) would be 32%.
ROE tells us how much profit a company is making for every dollar that is invested in it. So if ABC had $100 worth of shares and earned an ROE of 32%, then it would make $32 in profit for every dollar that was invested in it.
In summary, Dupont analysis helps us understand how a company makes money by breaking down the process into smaller parts: profit margin, asset turnover, and financial leverage which ultimately helps us calculate the Return on Equity (ROE).
