Equipotential
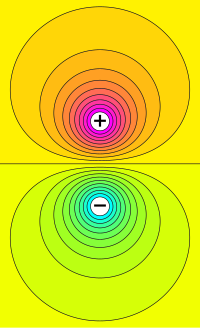
Have you ever played on a teeter-totter or seesaw with a friend? When you both sit at the same height on opposite sides, the board doesn't move because you are balanced. This is because you are on an "equipotential" surface, which means that you are at the same amount of height or energy.
Now, imagine a sloping hill that goes up and downhill. If you put a ball at the top of the hill, it will roll down to the bottom because it has more energy at the top, and less energy at the bottom. But if you put the ball on a flat surface, it will stay still because it has equal amounts of energy all around it. That flat surface is an equipotential surface because it has the same amount of energy everywhere on it.
In science, we use the term "equipotential" to talk about a surface or object where all the points on it have the same amount of energy or voltage. This is really important because it helps us understand how things move and how electricity works. By studying equipotential surfaces, scientists can figure out how to keep things balanced and how to make sure electricity flows safely from one place to another.
Now, imagine a sloping hill that goes up and downhill. If you put a ball at the top of the hill, it will roll down to the bottom because it has more energy at the top, and less energy at the bottom. But if you put the ball on a flat surface, it will stay still because it has equal amounts of energy all around it. That flat surface is an equipotential surface because it has the same amount of energy everywhere on it.
In science, we use the term "equipotential" to talk about a surface or object where all the points on it have the same amount of energy or voltage. This is really important because it helps us understand how things move and how electricity works. By studying equipotential surfaces, scientists can figure out how to keep things balanced and how to make sure electricity flows safely from one place to another.
Related topics others have asked about:
