Heat diffusion
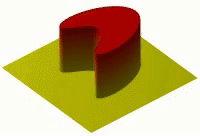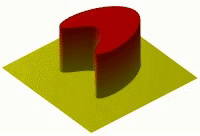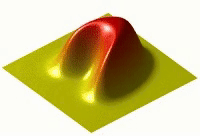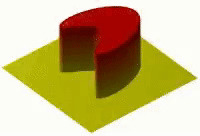
Okay, so imagine you have a hot plate of cookies that you just baked. If you put your hand right on the plate, it would be very hot and might even burn you! But if you wait a little while, the plate will start to cool down and the cookies won't be so hot anymore.
This is because the heat from the plate is spreading out, or diffusing, and moving from the hot cookie surface to the cooler air around it. Heat diffusion is basically how heat spreads out from a hot object to its cooler surroundings.
Heat is made up of tiny particles called molecules that move around really fast. When things are hot, those molecules are moving even faster than they would be if things were cooler. As those fast-moving molecules bump into slower-moving molecules around them, they start to transfer some of their energy, or heat, over to those other molecules. And when those molecules start to move faster, they bump into even slower-moving molecules around them and transfer some heat to them too, and so on and so on.
This process continues until the hot object has transferred most of its heat to the cooler surroundings around it. The heat diffuses through the air or other materials around it, moving from areas of higher temperature to areas of lower temperature until everything is more or less the same temperature.
So, in summary, heat diffusion is when heat moves from a hot object to the cooler surroundings around it, by way of the movement of tiny particles called molecules.
This is because the heat from the plate is spreading out, or diffusing, and moving from the hot cookie surface to the cooler air around it. Heat diffusion is basically how heat spreads out from a hot object to its cooler surroundings.
Heat is made up of tiny particles called molecules that move around really fast. When things are hot, those molecules are moving even faster than they would be if things were cooler. As those fast-moving molecules bump into slower-moving molecules around them, they start to transfer some of their energy, or heat, over to those other molecules. And when those molecules start to move faster, they bump into even slower-moving molecules around them and transfer some heat to them too, and so on and so on.
This process continues until the hot object has transferred most of its heat to the cooler surroundings around it. The heat diffuses through the air or other materials around it, moving from areas of higher temperature to areas of lower temperature until everything is more or less the same temperature.
So, in summary, heat diffusion is when heat moves from a hot object to the cooler surroundings around it, by way of the movement of tiny particles called molecules.
Related topics others have asked about:
