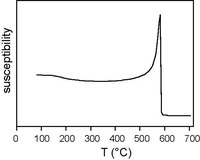
Hopkinson effect
Imagine you have two magnets - one on the top and the other on the bottom. If you push the magnets together, they'll stick because they're attracted to each other. If you try to pull the magnets apart, they'll stay stuck because they're still attracted to each other.
Now imagine you have a metal rod, and you put one magnet at one end, and the other magnet at the other end. If you try to pull the magnets apart, the metal rod will stretch like a rubber band, because the magnets are still strongly attracted to each other.
When you let go of the magnets, the metal rod will snap back to its original shape. This is called the Hopkinson Effect, and it happens because the magnetic force is very strong and can cause the metal to behave like a spring.
The Hopkinson Effect is important for things like guns and other weapons, because it allows them to fire bullets or projectiles at very high speeds. It's also used in scientific experiments to study the behavior of materials under extreme conditions.
Now imagine you have a metal rod, and you put one magnet at one end, and the other magnet at the other end. If you try to pull the magnets apart, the metal rod will stretch like a rubber band, because the magnets are still strongly attracted to each other.
When you let go of the magnets, the metal rod will snap back to its original shape. This is called the Hopkinson Effect, and it happens because the magnetic force is very strong and can cause the metal to behave like a spring.
The Hopkinson Effect is important for things like guns and other weapons, because it allows them to fire bullets or projectiles at very high speeds. It's also used in scientific experiments to study the behavior of materials under extreme conditions.
Related topics others have asked about:
