Kainate receptor
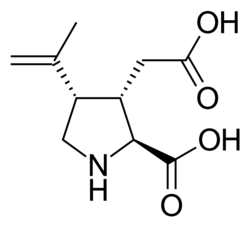
Okay, kiddo, it's time to learn about kainate receptors! Imagine your body is like a big building with lots of rooms, and each room has a special door that only certain keys can fit into. Kainate receptors are like the keys that fit into a special door in your brain cells called a "receptor". When the key goes into the lock (or receptor), it opens the door and lets something called a neurotransmitter come inside.
Now, this neurotransmitter is like a message that your brain cells use to talk to each other. When the neurotransmitter gets inside the cell, it can make the cell do different things - like talk louder or quieter, or turn on or off a light switch. Kainate receptors are special because they help control how much of the neurotransmitter gets let into the cell, and what happens when it gets there.
But, just like some keys can open lots of doors, kainate receptors can work in different parts of the brain and have different effects depending on where they are. Sometimes, they can make your brain cells work better and faster, but other times they can actually cause damage if they don't work right or if too much neurotransmitter gets in.
So, to sum it up - kainate receptors are like keys that unlock special doors in your brain cells, letting in messages that help your brain work. They can have different effects depending on where they are and how much neurotransmitter they let in, but overall they help keep your brain working properly.
Now, this neurotransmitter is like a message that your brain cells use to talk to each other. When the neurotransmitter gets inside the cell, it can make the cell do different things - like talk louder or quieter, or turn on or off a light switch. Kainate receptors are special because they help control how much of the neurotransmitter gets let into the cell, and what happens when it gets there.
But, just like some keys can open lots of doors, kainate receptors can work in different parts of the brain and have different effects depending on where they are. Sometimes, they can make your brain cells work better and faster, but other times they can actually cause damage if they don't work right or if too much neurotransmitter gets in.
So, to sum it up - kainate receptors are like keys that unlock special doors in your brain cells, letting in messages that help your brain work. They can have different effects depending on where they are and how much neurotransmitter they let in, but overall they help keep your brain working properly.
Related topics others have asked about:
