Nondisjunction
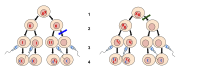
Nondisjunction happens when cells don't divide the way they're supposed to. Think of cells like tiny little Lego blocks that build all the different parts of your body. Normally, when your cells divide, they split apart and each new cell gets the same number of Lego blocks.
But sometimes, one of the cells doesn't get the right number of blocks. This can happen when the Lego blocks, or chromosomes, don't separate evenly during cell division. When this happens, one cell might get too many blocks, and another cell might not get enough.
This can be a problem, because having too many or too few blocks can cause problems with how your body works. It's kind of like if you had too many Legos to build your spaceship, or not enough to build your castle. It wouldn't work quite right.
Nondisjunction can happen in different parts of the body, and can cause different problems. For example, if it happens in the cells that make eggs or sperm, it can lead to genetic disorders in babies. Or, if it happens in other cells in the body, it can cause conditions like Down syndrome.
Scientists are still learning more about why nondisjunction happens, and how we can prevent it from causing problems. But for now, we can think of it like a mistake that happens when our Lego blocks don't divide the way they're supposed to.
But sometimes, one of the cells doesn't get the right number of blocks. This can happen when the Lego blocks, or chromosomes, don't separate evenly during cell division. When this happens, one cell might get too many blocks, and another cell might not get enough.
This can be a problem, because having too many or too few blocks can cause problems with how your body works. It's kind of like if you had too many Legos to build your spaceship, or not enough to build your castle. It wouldn't work quite right.
Nondisjunction can happen in different parts of the body, and can cause different problems. For example, if it happens in the cells that make eggs or sperm, it can lead to genetic disorders in babies. Or, if it happens in other cells in the body, it can cause conditions like Down syndrome.
Scientists are still learning more about why nondisjunction happens, and how we can prevent it from causing problems. But for now, we can think of it like a mistake that happens when our Lego blocks don't divide the way they're supposed to.
