Open system (systems theory)
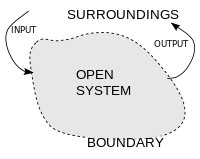
An open system is a system that interacts with its environment, exchanging energy and materials with the environment. It is the opposite of a closed system, which does not interact with its environment. The most common example of an open system is living things, such as us. We take in food, breathe air, and interact with other living things. We also give off energy and other materials, such as carbon dioxide.
Another example of an open system is a factory that produces goods. The factory takes in energy and materials (like raw materials) to make a product. The factory then gives off energy (like heat) and materials (like the finished product).
Open systems are important because they can change and adapt over time, which allows them to survive in their environment. Closed systems, on the other hand, can't adapt and are often more fragile.
Another example of an open system is a factory that produces goods. The factory takes in energy and materials (like raw materials) to make a product. The factory then gives off energy (like heat) and materials (like the finished product).
Open systems are important because they can change and adapt over time, which allows them to survive in their environment. Closed systems, on the other hand, can't adapt and are often more fragile.
Related topics others have asked about:
