Planckian locus
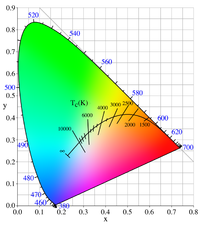
The Planckian Locus is like a path that shows all the different colors of light that can be produced by a glowing hot object, like a light bulb or the sun.
Imagine you have a magic box that can make things really hot and glowing. When you turn it on, it will start to produce light.
Now, if you carefully measure the color of the light produced over a long period of time, you will notice something really interesting. The color of the light changes as the temperature inside the box changes.
At first, the light is reddish (like a sunset), but as the temperature increases, the color shifts towards orange, then yellow, then white, and finally blue-white (like a bright blue sky).
This is because the higher the temperature gets, the more energy the light has, and the shorter the wavelength of the light becomes.
Scientists have observed this relationship between temperature and color for many different glowing hot objects, and have plotted all the different colors on a graph. This graph is called the Planckian Locus.
It looks like a curvy line that starts off red and ends up blue-white, and it shows us all the different colors we can get as we heat up our magic box.
So, the Planckian Locus is a tool that helps us understand how the color of light changes depending on the temperature of the light source. Pretty cool, right?
Imagine you have a magic box that can make things really hot and glowing. When you turn it on, it will start to produce light.
Now, if you carefully measure the color of the light produced over a long period of time, you will notice something really interesting. The color of the light changes as the temperature inside the box changes.
At first, the light is reddish (like a sunset), but as the temperature increases, the color shifts towards orange, then yellow, then white, and finally blue-white (like a bright blue sky).
This is because the higher the temperature gets, the more energy the light has, and the shorter the wavelength of the light becomes.
Scientists have observed this relationship between temperature and color for many different glowing hot objects, and have plotted all the different colors on a graph. This graph is called the Planckian Locus.
It looks like a curvy line that starts off red and ends up blue-white, and it shows us all the different colors we can get as we heat up our magic box.
So, the Planckian Locus is a tool that helps us understand how the color of light changes depending on the temperature of the light source. Pretty cool, right?
Related topics others have asked about:
