Plane stress
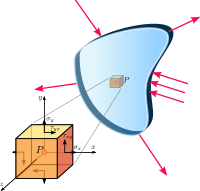
Okay, imagine you have a really thin piece of paper. You can easily bend it or fold it because it's so thin, right? But if you try to pull it apart or squish it too much, it might tear or break.
Now, let's think about a big metal plate instead of the piece of paper. If we only apply forces that are in the same plane as the plate (for example, pushing down on it or pulling it sideways), the plate will behave similarly to the paper. We call this "plane stress."
But if we try to apply forces that are perpendicular to the plane of the plate (like trying to push into the plate or pull it up from the bottom), that's called "out-of-plane stress." Just like the paper, the plate might start to deform or even break if it's subjected to too much out-of-plane stress.
So, in summary, plane stress is when we only apply forces in the same plane as a thin material like a metal plate, and out-of-plane stress is when we apply forces perpendicular to that plane. Understanding the difference is important for designing and analyzing structures and materials.
Now, let's think about a big metal plate instead of the piece of paper. If we only apply forces that are in the same plane as the plate (for example, pushing down on it or pulling it sideways), the plate will behave similarly to the paper. We call this "plane stress."
But if we try to apply forces that are perpendicular to the plane of the plate (like trying to push into the plate or pull it up from the bottom), that's called "out-of-plane stress." Just like the paper, the plate might start to deform or even break if it's subjected to too much out-of-plane stress.
So, in summary, plane stress is when we only apply forces in the same plane as a thin material like a metal plate, and out-of-plane stress is when we apply forces perpendicular to that plane. Understanding the difference is important for designing and analyzing structures and materials.
Related topics others have asked about:
