Q10 (temperature coefficient)
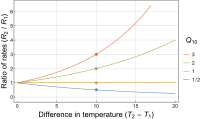
Q10 is a measure of how much faster or slower a chemical reaction, such as the process of breaking down food in our bodies, will go when the temperature changes.
Think of it like a cake baking in an oven. The recipe tells you to bake the cake at a certain temperature for a certain amount of time. If you were to turn up the heat in the oven, the cake would cook faster because the temperature is higher. On the other hand, if you were to lower the heat, the cake would take longer to cook.
Q10 works similarly. It tells us how much faster or slower a reaction will go if the temperature is increased or decreased by a certain amount. For example, if Q10 is 2, that means that for every 10 degrees Celsius (or 18 degrees Fahrenheit) increase in temperature, the reaction will happen twice as fast.
This can be important in many different situations. For example, scientists use Q10 to understand how temperature changes affect the growth and survival of plants and animals. They can use this information to predict how things like climate change might impact different species.
Overall, Q10 is simply a way to measure how much temperature affects the speed of chemical reactions in different systems.
Think of it like a cake baking in an oven. The recipe tells you to bake the cake at a certain temperature for a certain amount of time. If you were to turn up the heat in the oven, the cake would cook faster because the temperature is higher. On the other hand, if you were to lower the heat, the cake would take longer to cook.
Q10 works similarly. It tells us how much faster or slower a reaction will go if the temperature is increased or decreased by a certain amount. For example, if Q10 is 2, that means that for every 10 degrees Celsius (or 18 degrees Fahrenheit) increase in temperature, the reaction will happen twice as fast.
This can be important in many different situations. For example, scientists use Q10 to understand how temperature changes affect the growth and survival of plants and animals. They can use this information to predict how things like climate change might impact different species.
Overall, Q10 is simply a way to measure how much temperature affects the speed of chemical reactions in different systems.
Related topics others have asked about:
