Residue curve
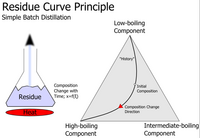
Residue curves are like a map that shows us what happens to a substance when it is being heated up and cooled down. Think of a pan of water on the stove. When we heat up the water, it starts to boil and turn into steam. This is because the water is changing from a liquid to a gas.
The same thing happens to other substances when we heat them up. For example, if we heat up a mixture of two chemicals, they might change from a liquid to a gas at different temperatures. We can use a residue curve to see how these two chemicals will behave when we heat them up and cool them down.
Residue curves are like a graph that shows us the temperature and pressure needed to turn a substance from a liquid to a gas. We can use this graph to predict how a substance will behave under different conditions. For example, if we know that a certain chemical will turn into a gas at a certain temperature and pressure, we can use this information to design a process to separate that chemical from other chemicals in a mixture.
So, to sum up, a residue curve is a graph that helps us understand how a substance will behave when we heat it up and cool it down. It helps us design processes for separating chemicals and other substances.
The same thing happens to other substances when we heat them up. For example, if we heat up a mixture of two chemicals, they might change from a liquid to a gas at different temperatures. We can use a residue curve to see how these two chemicals will behave when we heat them up and cool them down.
Residue curves are like a graph that shows us the temperature and pressure needed to turn a substance from a liquid to a gas. We can use this graph to predict how a substance will behave under different conditions. For example, if we know that a certain chemical will turn into a gas at a certain temperature and pressure, we can use this information to design a process to separate that chemical from other chemicals in a mixture.
So, to sum up, a residue curve is a graph that helps us understand how a substance will behave when we heat it up and cool it down. It helps us design processes for separating chemicals and other substances.
