Roche lobe
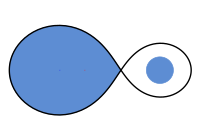
Okay kiddo, so let's talk about something called Roche lobe. Imagine you have two friends, let's call them star 1 and star 2, who are really close to each other, like holding hands. They love each other so much that they are attracted to each other and they start orbiting around each other. Now, sometimes in this relationship, one star may be bigger than the other, and this can create a problem.
Let's say star 1 is bigger than star 2. Because star 1 is bigger, it has more gravity than star 2, and it can pull gas and material from star 2 towards itself. This is called accretion. But there's a limit to how much gas and material star 1 can pull from star 2. This limit is called the Roche lobe.
Imagine a big bubble around each star, like a giant balloon. The Roche lobe is the imaginary line that separates the gas and material that star 1 can pull from star 2 from the gas and material that is held by the gravity of star 2.
Now, if a star passes its Roche lobe, it can start sucking up gas and material from its partner star, kind of like slurping up a milkshake. This can cause some pretty interesting effects, like making the star brighter or even causing an explosion!
So, the Roche lobe is basically the limit of how much material one star can take from another star in a binary star system. In simple terms, it's like a protective bubble around each star that keeps their gas and material safe.
Let's say star 1 is bigger than star 2. Because star 1 is bigger, it has more gravity than star 2, and it can pull gas and material from star 2 towards itself. This is called accretion. But there's a limit to how much gas and material star 1 can pull from star 2. This limit is called the Roche lobe.
Imagine a big bubble around each star, like a giant balloon. The Roche lobe is the imaginary line that separates the gas and material that star 1 can pull from star 2 from the gas and material that is held by the gravity of star 2.
Now, if a star passes its Roche lobe, it can start sucking up gas and material from its partner star, kind of like slurping up a milkshake. This can cause some pretty interesting effects, like making the star brighter or even causing an explosion!
So, the Roche lobe is basically the limit of how much material one star can take from another star in a binary star system. In simple terms, it's like a protective bubble around each star that keeps their gas and material safe.
