Sankey diagram
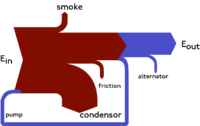
A Sankey diagram is a way to show how things move or change from one state to another. Imagine you have some apples and you want to show how many of them are eaten, how many are used for cooking, and how many are left over. You can draw a Sankey diagram to help you see that information.
The top of the diagram shows the total number of apples you started with. Then there are arrows going down to show where the apples went. For example, some of the arrows might go to "eaten," "cooked," or "left over." The thickness of the arrows represents the amount of apples that went into each category. So if a lot of the apples were eaten, the arrow pointing to "eaten" would be thicker.
The bottom of the diagram shows how many apples are left over. This is important to help you see if everything adds up correctly. If you started with 10 apples and you know you ate 6 and cooked 2, then you should have 2 left over. The diagram can help you see if that's true.
Sankey diagrams can be used for lots of different things besides apples. They are great for showing how energy is used in a building, how water flows through a system, or how money is spent in a budget. The key is to have different categories that the items you're looking at can be grouped into. Then you can see where everything goes and how it all fits together.
The top of the diagram shows the total number of apples you started with. Then there are arrows going down to show where the apples went. For example, some of the arrows might go to "eaten," "cooked," or "left over." The thickness of the arrows represents the amount of apples that went into each category. So if a lot of the apples were eaten, the arrow pointing to "eaten" would be thicker.
The bottom of the diagram shows how many apples are left over. This is important to help you see if everything adds up correctly. If you started with 10 apples and you know you ate 6 and cooked 2, then you should have 2 left over. The diagram can help you see if that's true.
Sankey diagrams can be used for lots of different things besides apples. They are great for showing how energy is used in a building, how water flows through a system, or how money is spent in a budget. The key is to have different categories that the items you're looking at can be grouped into. Then you can see where everything goes and how it all fits together.
Related topics others have asked about:
