Serpentine geometry plasma actuator
Imagine you have a toy car and you want it to go faster. You can push it with your hand, but that only works for a little bit. What if instead, you could make the air around the car push it forward? That's kind of like what a serpentine geometry plasma actuator does.
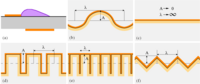
A serpentine geometry plasma actuator is a special device that uses electricity to create a special kind of gas called plasma. This plasma is made up of really hot, charged particles that can interact with the air around it. When the plasma is created in a serpentine geometry plasma actuator, it forms a special shape that looks like a winding snake (also called a "serpentine").
This special shape is important because it can interact with the air in a special way. When the plasma is turned on, it ionizes the air molecules nearby. This means it makes them positively or negatively charged. This creates a kind of "wind" that can push things around.
Scientists use this kind of actuator when they want to control the flow of air around something. For example, imagine an airplane wing or a car. The way air flows around these objects is very important for how they work. If you can control the flow of air, you can make them more efficient or faster.
By using a serpentine geometry plasma actuator, scientists can control how the air flows around these objects. The plasma creates a "wind" that pushes the air in a certain direction. This can help lift an airplane off the ground or make a car go faster.
So, in short, a serpentine geometry plasma actuator is a device that creates a special kind of gas that can interact with the air around it to control the flow of air around objects like airplanes or cars.
A serpentine geometry plasma actuator is a special device that uses electricity to create a special kind of gas called plasma. This plasma is made up of really hot, charged particles that can interact with the air around it. When the plasma is created in a serpentine geometry plasma actuator, it forms a special shape that looks like a winding snake (also called a "serpentine").
This special shape is important because it can interact with the air in a special way. When the plasma is turned on, it ionizes the air molecules nearby. This means it makes them positively or negatively charged. This creates a kind of "wind" that can push things around.
Scientists use this kind of actuator when they want to control the flow of air around something. For example, imagine an airplane wing or a car. The way air flows around these objects is very important for how they work. If you can control the flow of air, you can make them more efficient or faster.
By using a serpentine geometry plasma actuator, scientists can control how the air flows around these objects. The plasma creates a "wind" that pushes the air in a certain direction. This can help lift an airplane off the ground or make a car go faster.
So, in short, a serpentine geometry plasma actuator is a device that creates a special kind of gas that can interact with the air around it to control the flow of air around objects like airplanes or cars.
Related topics others have asked about:
