Signal transduction
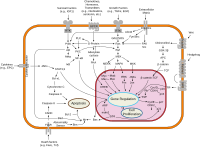
Signal transduction is when the cells in our body talk to each other. It's like when you talk to your friend on the phone, and you tell them something important, and then they tell their other friends, who then tell even more friends, until a lot of people know what you said.
In your body, this happens in a much more complicated way. It starts when one cell sends a message, called a signal, to another cell. This signal can be sent in different ways, like through chemicals or electrical impulses.
When the second cell gets the signal, it has to figure out what to do with it. It does this by using special proteins and molecules inside the cell called receptors. These receptors are like tiny switches that turn on when they sense the signal.
Once the receptor is turned on, it sends a message inside the cell. This message can go to lots of different parts of the cell, like the nucleus or the mitochondria. The message tells the cell what to do next, like make more of a certain protein or start breaking down some waste material.
This whole process of sending a signal, receiving it with a receptor, and sending a message inside the cell is called signal transduction. It's like a game of telephone, except instead of saying the same message over and over, each cell is getting a unique message and responding in a specific way.
Signal transduction is really important for how our body works. It helps cells communicate with each other so they can do important things like fight off infections, heal wounds, and grow and develop properly.
In your body, this happens in a much more complicated way. It starts when one cell sends a message, called a signal, to another cell. This signal can be sent in different ways, like through chemicals or electrical impulses.
When the second cell gets the signal, it has to figure out what to do with it. It does this by using special proteins and molecules inside the cell called receptors. These receptors are like tiny switches that turn on when they sense the signal.
Once the receptor is turned on, it sends a message inside the cell. This message can go to lots of different parts of the cell, like the nucleus or the mitochondria. The message tells the cell what to do next, like make more of a certain protein or start breaking down some waste material.
This whole process of sending a signal, receiving it with a receptor, and sending a message inside the cell is called signal transduction. It's like a game of telephone, except instead of saying the same message over and over, each cell is getting a unique message and responding in a specific way.
Signal transduction is really important for how our body works. It helps cells communicate with each other so they can do important things like fight off infections, heal wounds, and grow and develop properly.
Related topics others have asked about:
