Theory of solar cell
Have you ever used a calculator powered by solar energy, where the numbers show up when you place the calculator in the sunlight? Well, a solar cell is like a tiny calculator. It can turn sunlight into electricity!
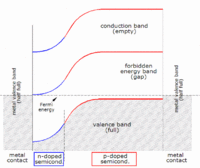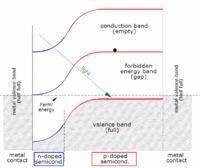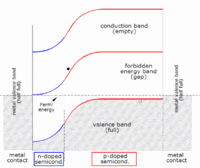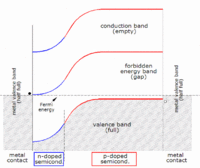
The idea behind solar cells is that silicon is a material that can conduct electricity when light hits it, creating a flow of electrons. This flow of electrons is called an electric current. The basic parts of a solar cell are silicon and wires. The silicon is the part that gets hit by the sunlight, and the wires are what the electricity flows through.
When light hits the silicon in a solar cell, it knocks some electrons loose from the atoms in the silicon. These free electrons flow into the wires, creating an electric current. The solar cell is built with a positive side and a negative side, just like a battery, and the electric current created by the flow of electrons goes from one side to the other.
But how do we get enough power from a small solar cell? Solar cells can be connected together to make a solar panel, which is like a bunch of solar cells working together. The more solar cells you have connected, the more electricity you can produce.
In summary, a solar cell is like a tiny calculator that turns sunlight into electricity by using silicon and wires. When light hits the silicon, it knocks some electrons loose, creating an electric current that can be used as energy. When a bunch of solar cells are connected together, they can make a larger solar panel that can produce even more electricity!
The idea behind solar cells is that silicon is a material that can conduct electricity when light hits it, creating a flow of electrons. This flow of electrons is called an electric current. The basic parts of a solar cell are silicon and wires. The silicon is the part that gets hit by the sunlight, and the wires are what the electricity flows through.
When light hits the silicon in a solar cell, it knocks some electrons loose from the atoms in the silicon. These free electrons flow into the wires, creating an electric current. The solar cell is built with a positive side and a negative side, just like a battery, and the electric current created by the flow of electrons goes from one side to the other.
But how do we get enough power from a small solar cell? Solar cells can be connected together to make a solar panel, which is like a bunch of solar cells working together. The more solar cells you have connected, the more electricity you can produce.
In summary, a solar cell is like a tiny calculator that turns sunlight into electricity by using silicon and wires. When light hits the silicon, it knocks some electrons loose, creating an electric current that can be used as energy. When a bunch of solar cells are connected together, they can make a larger solar panel that can produce even more electricity!
Related topics others have asked about:
