Varieties of Arabic
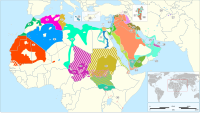
Arabic is a language that is spoken in many different countries and regions, and different parts of the world may use different dialects or versions of the language. Each dialect or version of Arabic is known as a variety.
Some of the most common Arab varieties include:
- Modern Standard Arabic (MSA): This is the "official" version of Arabic that is used for formal writing, news broadcasts, and in some educational settings.
- Classical Arabic: This is the language of the Quran and is used for religious purposes.
- Gulf Arabic: This is a variety of Arabic that is spoken in the Gulf countries, such as Kuwait, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates. It has its own distinct pronunciation and vocabulary.
- Egyptian Arabic: This is a variety of Arabic that is spoken in Egypt, and is often used in movies and television shows. It has its own unique words and phrases that are not found in other varieties of Arabic.
- Levantine Arabic: This variety of Arabic is spoken in countries such as Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria. It has its own distinct pronunciation and vocabulary.
Each variety of Arabic can be very different from the others. For example, the pronunciation of words may vary from one region to another, and there may be different words for the same thing. This means that people who speak one variety of Arabic may not always understand people who speak a different variety. However, most Arabic speakers can understand Modern Standard Arabic, which is used in formal settings throughout the Arab world.
Some of the most common Arab varieties include:
- Modern Standard Arabic (MSA): This is the "official" version of Arabic that is used for formal writing, news broadcasts, and in some educational settings.
- Classical Arabic: This is the language of the Quran and is used for religious purposes.
- Gulf Arabic: This is a variety of Arabic that is spoken in the Gulf countries, such as Kuwait, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates. It has its own distinct pronunciation and vocabulary.
- Egyptian Arabic: This is a variety of Arabic that is spoken in Egypt, and is often used in movies and television shows. It has its own unique words and phrases that are not found in other varieties of Arabic.
- Levantine Arabic: This variety of Arabic is spoken in countries such as Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria. It has its own distinct pronunciation and vocabulary.
Each variety of Arabic can be very different from the others. For example, the pronunciation of words may vary from one region to another, and there may be different words for the same thing. This means that people who speak one variety of Arabic may not always understand people who speak a different variety. However, most Arabic speakers can understand Modern Standard Arabic, which is used in formal settings throughout the Arab world.
Related topics others have asked about:
