Antisymmetric exchange
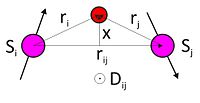
Antisymmetric exchange is when two very small particles called electrons interact with each other in a way that causes one of the electrons to be "up" and the other to be "down". Think of it like a see-saw: when one end goes up, the other end goes down.
This happens because electrons have something called "spin". Spin is a lot like how a top spins around on a table, except it happens inside the electron. When two electrons interact, their spins can either be pointing in the same direction or in opposite directions. If they're pointing in opposite directions, we say that the interaction is "antisymmetric".
Scientists study antisymmetric exchange because it can help us understand how magnets work. Magnets are materials that have a lot of electrons with spins pointing in the same direction. Antisymmetric exchange can help us figure out how these electrons get their spins to line up in the same direction, and why magnets have different strengths.
Overall, antisymmetric exchange is a fancy way of saying that electrons can influence each other's spins. It's like a game of spin the top, but with electrons instead!
This happens because electrons have something called "spin". Spin is a lot like how a top spins around on a table, except it happens inside the electron. When two electrons interact, their spins can either be pointing in the same direction or in opposite directions. If they're pointing in opposite directions, we say that the interaction is "antisymmetric".
Scientists study antisymmetric exchange because it can help us understand how magnets work. Magnets are materials that have a lot of electrons with spins pointing in the same direction. Antisymmetric exchange can help us figure out how these electrons get their spins to line up in the same direction, and why magnets have different strengths.
Overall, antisymmetric exchange is a fancy way of saying that electrons can influence each other's spins. It's like a game of spin the top, but with electrons instead!
Related topics others have asked about:
