Arc elasticity
Imagine you have a rubber band. When you stretch the rubber band a little bit, it gets slightly longer, but not a lot longer. But if you keep stretching the rubber band, it starts to get longer and longer. When you stretch a rubber band a lot, the change in length is much greater than when you only stretch it a little bit.
Elasticity is how much something can stretch or change when you pull on it.
Now, let's talk about arc elasticity. When we measure the elasticity of something, we can measure it in two different ways: "point elasticity" and "arc elasticity."
Point elasticity is just measuring how much something changes at one specific point. For example, let's say we want to measure the point elasticity of a rubber band - we could measure how much it stretches when we pull on it at one spot.
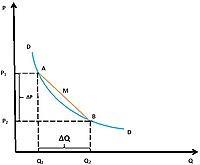
But sometimes we need to measure elasticity across a range of values, not just at one specific point. This is where arc elasticity comes in. Arc elasticity measures how much something changes as we move across a range of values.
For example, let's use a different example: the price of a toy. If the price of the toy goes up by one dollar, some people might still buy it, but other people might not be willing to pay the extra dollar. But if the price goes up by five dollars, even more people might decide not to buy it. Arc elasticity measures how much the quantity of toys sold changes as the price changes across a range of values, not just at one specific price point.
So, arc elasticity is like stretching a rubber band a lot and measuring how much it changes at different levels of stretching. We can measure elasticity in different ways, and arc elasticity helps us measure how much something changes over a range of values.
Elasticity is how much something can stretch or change when you pull on it.
Now, let's talk about arc elasticity. When we measure the elasticity of something, we can measure it in two different ways: "point elasticity" and "arc elasticity."
Point elasticity is just measuring how much something changes at one specific point. For example, let's say we want to measure the point elasticity of a rubber band - we could measure how much it stretches when we pull on it at one spot.
But sometimes we need to measure elasticity across a range of values, not just at one specific point. This is where arc elasticity comes in. Arc elasticity measures how much something changes as we move across a range of values.
For example, let's use a different example: the price of a toy. If the price of the toy goes up by one dollar, some people might still buy it, but other people might not be willing to pay the extra dollar. But if the price goes up by five dollars, even more people might decide not to buy it. Arc elasticity measures how much the quantity of toys sold changes as the price changes across a range of values, not just at one specific price point.
So, arc elasticity is like stretching a rubber band a lot and measuring how much it changes at different levels of stretching. We can measure elasticity in different ways, and arc elasticity helps us measure how much something changes over a range of values.
Related topics others have asked about:
