Asian Dust
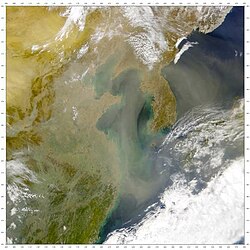
Asian dust, also known as yellow dust or fine particulate matter, is basically dirt and sand particles that get blown up into the air from the deserts and dry areas of East Asia. This can happen when strong winds blow across these regions and pick up dirt and sand particles, which can then travel long distances and affect other parts of the world.
The main sources of Asian dust are the Gobi and Taklamakan deserts in China and Mongolia, as well as the deserts in North Korea, South Korea, and Japan. These regions are very dry and have very little vegetation, which means that the soil is loose and can easily be picked up by the wind.
When these dust particles are in the air, they can cause a lot of problems for people and the environment. This is because they are very small and can easily get into our bodies and cause respiratory problems, especially for people with asthma or allergies. They can also cause problems for plants and animals, by depriving them of sunlight and clogging up their respiratory systems.
In addition to health and environmental problems, Asian dust can also have economic impacts. For example, it can cause problems for transportation and agriculture by making roads and crops dusty and reducing visibility. This can lead to reduced productivity and increased costs for farmers and businesses.
Overall, Asian dust is a natural phenomenon that can have both positive and negative effects on the environment and human health. While we can't stop it from happening, we can take steps to reduce its impact by wearing masks, using air filters, and reducing our carbon emissions.
The main sources of Asian dust are the Gobi and Taklamakan deserts in China and Mongolia, as well as the deserts in North Korea, South Korea, and Japan. These regions are very dry and have very little vegetation, which means that the soil is loose and can easily be picked up by the wind.
When these dust particles are in the air, they can cause a lot of problems for people and the environment. This is because they are very small and can easily get into our bodies and cause respiratory problems, especially for people with asthma or allergies. They can also cause problems for plants and animals, by depriving them of sunlight and clogging up their respiratory systems.
In addition to health and environmental problems, Asian dust can also have economic impacts. For example, it can cause problems for transportation and agriculture by making roads and crops dusty and reducing visibility. This can lead to reduced productivity and increased costs for farmers and businesses.
Overall, Asian dust is a natural phenomenon that can have both positive and negative effects on the environment and human health. While we can't stop it from happening, we can take steps to reduce its impact by wearing masks, using air filters, and reducing our carbon emissions.
Related topics others have asked about:
