Bidirectional scattering distribution function
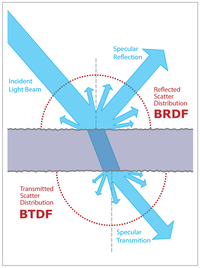
Have you ever played with a flashlight and seen how the light goes different ways when you shine it on different things? That's kind of like the bidirectional scattering distribution function!
Okay, let's break it down a bit.
Bidirectional just means that we're looking at how the light is going in two directions at once. For example, if you shine a light on a ball, some of the light will bounce back towards your eyes (we call this the "backscatter" direction), and some of the light will bounce off in other directions.
Scattering is what happens when light hits something and then goes in a different direction. Think about how a ball bounces off a wall - the wall is scattering the ball's movement.
Distribution function just means that we're looking at how much light is going in each direction. So for our ball example, we might want to know how much of the light is going straight back towards our eyes, versus how much is going off to the side.
Put it all together, and the bidirectional scattering distribution function (BSDF) is a way of describing how light interacts with different surfaces. It tells us how much light will be scattered in different directions when it hits a surface, which can be helpful for things like computer graphics or designing better lighting systems.
So next time you shine a flashlight around, remember that the BSDF is hard at work figuring out where all that light is going!
Okay, let's break it down a bit.
Bidirectional just means that we're looking at how the light is going in two directions at once. For example, if you shine a light on a ball, some of the light will bounce back towards your eyes (we call this the "backscatter" direction), and some of the light will bounce off in other directions.
Scattering is what happens when light hits something and then goes in a different direction. Think about how a ball bounces off a wall - the wall is scattering the ball's movement.
Distribution function just means that we're looking at how much light is going in each direction. So for our ball example, we might want to know how much of the light is going straight back towards our eyes, versus how much is going off to the side.
Put it all together, and the bidirectional scattering distribution function (BSDF) is a way of describing how light interacts with different surfaces. It tells us how much light will be scattered in different directions when it hits a surface, which can be helpful for things like computer graphics or designing better lighting systems.
So next time you shine a flashlight around, remember that the BSDF is hard at work figuring out where all that light is going!
Related topics others have asked about:
