Concrete fracture analysis
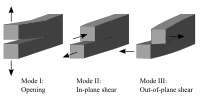
Concrete is a very strong and sturdy material that is used to build structures like buildings, bridges, and roads. However, sometimes it can break or crack, which is not good. When this happens, people need to figure out why the concrete broke and how to fix it so that it doesn't break again. This is what concrete fracture analysis is all about.
Think of concrete like a bunch of Lego blocks stuck together with glue. If you drop your Lego tower, the blocks might come apart, but the glue will hold them together. The glue in concrete is called cement, and it is mixed with sand and gravel to make a strong and hard material.
When concrete breaks, it can be because the glue (cement) is not strong enough, or because there is something else going on that is making the concrete weaker. Scientists and engineers study concrete fractures to figure out why it broke and what can be done to prevent it from happening again.
To study concrete fractures, researchers might look at a small piece of concrete under a microscope to see how the cement and other materials are arranged. They might also test the concrete in a lab to see how much weight it can hold before it breaks, or how much it stretches before it snaps.
By studying concrete fractures, scientists and engineers can figure out how to make better concrete that is less likely to break, and how to fix broken concrete so that it is just as strong as it was before. This helps keep buildings, bridges, and roads safe for people to use.
Think of concrete like a bunch of Lego blocks stuck together with glue. If you drop your Lego tower, the blocks might come apart, but the glue will hold them together. The glue in concrete is called cement, and it is mixed with sand and gravel to make a strong and hard material.
When concrete breaks, it can be because the glue (cement) is not strong enough, or because there is something else going on that is making the concrete weaker. Scientists and engineers study concrete fractures to figure out why it broke and what can be done to prevent it from happening again.
To study concrete fractures, researchers might look at a small piece of concrete under a microscope to see how the cement and other materials are arranged. They might also test the concrete in a lab to see how much weight it can hold before it breaks, or how much it stretches before it snaps.
By studying concrete fractures, scientists and engineers can figure out how to make better concrete that is less likely to break, and how to fix broken concrete so that it is just as strong as it was before. This helps keep buildings, bridges, and roads safe for people to use.
Related topics others have asked about:
