Depolarization
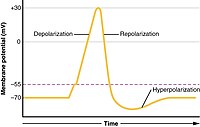
Okay kiddo, let's talk about depolarization.
First, we need to understand what happens in our brains. Our brains have lots of tiny little cells called neurons that talk to each other to help us think and do things. When they talk to each other, they send little electrical signals.
Now, each neuron has a tiny part called the cell membrane. Think of it like a fence around a house, it keeps things inside and outside separate. When a signal comes along, it can cross the fence and go inside the neuron.
Inside the neuron, there are things called ions. These are tiny little particles that have a charge, either positive or negative.
Normally, there are more negative ions inside the neuron and more positive ions outside. This keeps things balanced and means the neuron isn't firing signals all the time.
But when a signal comes along, it opens up little doors in the cell membrane and allows positive ions to rush into the neuron. This makes the inside of the neuron more positive than the outside, which is called depolarization.
Depolarization is important because it helps the signal travel along from one neuron to another. When one neuron depolarizes, it makes the adjacent neuron more likely to depolarize too.
So, depolarization is like a domino effect that helps our brains work properly. Without it, we wouldn't be able to think or do things!
First, we need to understand what happens in our brains. Our brains have lots of tiny little cells called neurons that talk to each other to help us think and do things. When they talk to each other, they send little electrical signals.
Now, each neuron has a tiny part called the cell membrane. Think of it like a fence around a house, it keeps things inside and outside separate. When a signal comes along, it can cross the fence and go inside the neuron.
Inside the neuron, there are things called ions. These are tiny little particles that have a charge, either positive or negative.
Normally, there are more negative ions inside the neuron and more positive ions outside. This keeps things balanced and means the neuron isn't firing signals all the time.
But when a signal comes along, it opens up little doors in the cell membrane and allows positive ions to rush into the neuron. This makes the inside of the neuron more positive than the outside, which is called depolarization.
Depolarization is important because it helps the signal travel along from one neuron to another. When one neuron depolarizes, it makes the adjacent neuron more likely to depolarize too.
So, depolarization is like a domino effect that helps our brains work properly. Without it, we wouldn't be able to think or do things!
