Double-exchange mechanism
Okay kiddo, have you ever played with magnets and noticed that sometimes they stick together and sometimes they push each other away? This happens because of something called magnetic interactions.
A double-exchange mechanism is a way that magnetic interaction can cause some materials to act like magnets. Imagine you have a bunch of tiny magnets, all spinning around in different directions. Sometimes they will all end up pointing in the same direction, creating a magnetic field. But sometimes they will cancel each other out and there won't be a magnetic field.
In some materials, like certain types of metal oxides, the magnetic interactions between the magnets are really strong, and they can cause some of the magnets to flip their direction so that they all end up pointing in the same direction. This creates a magnetic field that you can see and feel.
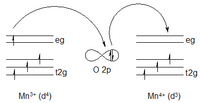
This flipping back and forth of the magnets is called a double-exchange mechanism, because two things have to happen for it to work. First, the electrons in the metal oxide have to be able to move around freely, so they can interact with each other. Second, there has to be a difference in energy between the two possible directions the magnets can point in. This difference in energy makes it possible for some of the magnets to flip their direction and create a magnetic field.
So, to sum up, a double-exchange mechanism is a way that magnetic interactions between tiny magnets can cause certain materials to act like magnets. It happens when the electrons in the material can move around freely and there's a difference in energy between the possible directions the magnets can point in.
A double-exchange mechanism is a way that magnetic interaction can cause some materials to act like magnets. Imagine you have a bunch of tiny magnets, all spinning around in different directions. Sometimes they will all end up pointing in the same direction, creating a magnetic field. But sometimes they will cancel each other out and there won't be a magnetic field.
In some materials, like certain types of metal oxides, the magnetic interactions between the magnets are really strong, and they can cause some of the magnets to flip their direction so that they all end up pointing in the same direction. This creates a magnetic field that you can see and feel.
This flipping back and forth of the magnets is called a double-exchange mechanism, because two things have to happen for it to work. First, the electrons in the metal oxide have to be able to move around freely, so they can interact with each other. Second, there has to be a difference in energy between the two possible directions the magnets can point in. This difference in energy makes it possible for some of the magnets to flip their direction and create a magnetic field.
So, to sum up, a double-exchange mechanism is a way that magnetic interactions between tiny magnets can cause certain materials to act like magnets. It happens when the electrons in the material can move around freely and there's a difference in energy between the possible directions the magnets can point in.
