Inverted yield curve
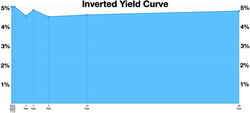
An inverted yield curve is a way to tell whether the economy is doing well or not.
Let's imagine you have some money and you want to lend it to someone for a certain amount of time. The person who borrows your money will pay you back the original amount plus some extra money, called interest. The amount of interest they need to pay you depends on how long they want to borrow the money for.
If the person wants to borrow the money for a shorter time, they will pay you less interest because they will return the money sooner. If they want to borrow the money for a longer time, they will pay you more interest because they will keep your money for a longer time.
Now, imagine that many people want to borrow money and they are all offering to pay different amounts of interest depending on how long they want to borrow it for. Some people want to borrow the money for a short time, while others want to borrow it for a long time.
The interest rates that people offer to pay can be used to create a graph called a yield curve. This graph shows how much interest people are willing to pay for different lengths of time.
Normally, the yield curve is upward sloping. This means that people are willing to pay more interest for longer borrowing periods, which is a sign that they are confident about the economy's future.
However, sometimes the yield curve can invert. This means that people are willing to pay more interest for shorter borrowing periods than for longer borrowing periods. This is a sign that people are not confident about the economy's future and are trying to protect their money by lending it for shorter periods instead of longer periods.
Inverted yield curves can be a sign that a recession is coming, because people are not willing to make long-term investments. This can affect businesses and individuals, making it harder for them to get loans or make investments, which can lead to a slowdown in economic growth.
Let's imagine you have some money and you want to lend it to someone for a certain amount of time. The person who borrows your money will pay you back the original amount plus some extra money, called interest. The amount of interest they need to pay you depends on how long they want to borrow the money for.
If the person wants to borrow the money for a shorter time, they will pay you less interest because they will return the money sooner. If they want to borrow the money for a longer time, they will pay you more interest because they will keep your money for a longer time.
Now, imagine that many people want to borrow money and they are all offering to pay different amounts of interest depending on how long they want to borrow it for. Some people want to borrow the money for a short time, while others want to borrow it for a long time.
The interest rates that people offer to pay can be used to create a graph called a yield curve. This graph shows how much interest people are willing to pay for different lengths of time.
Normally, the yield curve is upward sloping. This means that people are willing to pay more interest for longer borrowing periods, which is a sign that they are confident about the economy's future.
However, sometimes the yield curve can invert. This means that people are willing to pay more interest for shorter borrowing periods than for longer borrowing periods. This is a sign that people are not confident about the economy's future and are trying to protect their money by lending it for shorter periods instead of longer periods.
Inverted yield curves can be a sign that a recession is coming, because people are not willing to make long-term investments. This can affect businesses and individuals, making it harder for them to get loans or make investments, which can lead to a slowdown in economic growth.
Related topics others have asked about:
