Mechanical equilibrium
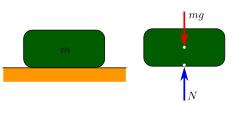
Mechanical equilibrium is when things are not moving. Think about when you try to balance a toy on your finger. You need the toy to be perfectly still and not falling off. This is a state of mechanical equilibrium.
There are two types of mechanical equilibrium: static and dynamic. Static equilibrium is when things are not moving at all. Dynamic equilibrium is when things are moving but not changing speed.
To understand mechanical equilibrium, you need to think about forces. Forces are things that push or pull things. When you push a toy, you are applying a force. If you pull a toy, you are also applying a force. Forces can make things move, stop moving, speed up, or slow down.
When things are in mechanical equilibrium, all the forces acting on the object cancel out. For example, if you are trying to balance a toy on your finger, you have to make sure that the force of gravity pulling the toy down is balanced by the force of your finger pushing the toy up. If these two forces are equal, then the toy will not move and you have achieved mechanical equilibrium.
In summary, mechanical equilibrium is a state where things are not moving, and all the forces acting on the object are balanced. It is important to understand the concept of mechanical equilibrium to understand why things move or don't move and how we can balance things.
There are two types of mechanical equilibrium: static and dynamic. Static equilibrium is when things are not moving at all. Dynamic equilibrium is when things are moving but not changing speed.
To understand mechanical equilibrium, you need to think about forces. Forces are things that push or pull things. When you push a toy, you are applying a force. If you pull a toy, you are also applying a force. Forces can make things move, stop moving, speed up, or slow down.
When things are in mechanical equilibrium, all the forces acting on the object cancel out. For example, if you are trying to balance a toy on your finger, you have to make sure that the force of gravity pulling the toy down is balanced by the force of your finger pushing the toy up. If these two forces are equal, then the toy will not move and you have achieved mechanical equilibrium.
In summary, mechanical equilibrium is a state where things are not moving, and all the forces acting on the object are balanced. It is important to understand the concept of mechanical equilibrium to understand why things move or don't move and how we can balance things.
Related topics others have asked about:
