Motor proteins
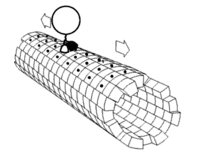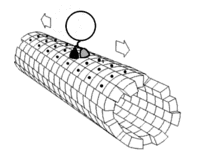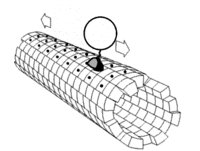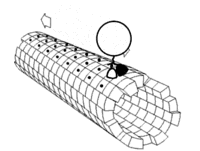
Motor proteins are like tiny trucks that carry items around inside of our cells. These proteins use energy to move along structures called microtubules which act like roads inside of the cell.
There are a few different types of motor proteins, but one of the most common is called kinesin. Kinesin has two feet, or "heads," that attach to the microtubules and then walk along them. One of the feet always stays connected to the microtubule while the other moves forward, like taking steps.
Another type of motor protein, called dynein, moves in the opposite direction of kinesin, allowing for transport in different directions within the cell.
Motor proteins can carry things like packages of proteins or organelles, like the mitochondria (the part of the cell that makes energy), from one part of the cell to another. They can also help shape the cell and move chromosomes during cell division.
Overall, motor proteins are like busy transport trucks that help keep our cells organized and functioning properly!
There are a few different types of motor proteins, but one of the most common is called kinesin. Kinesin has two feet, or "heads," that attach to the microtubules and then walk along them. One of the feet always stays connected to the microtubule while the other moves forward, like taking steps.
Another type of motor protein, called dynein, moves in the opposite direction of kinesin, allowing for transport in different directions within the cell.
Motor proteins can carry things like packages of proteins or organelles, like the mitochondria (the part of the cell that makes energy), from one part of the cell to another. They can also help shape the cell and move chromosomes during cell division.
Overall, motor proteins are like busy transport trucks that help keep our cells organized and functioning properly!
Related topics others have asked about:
