Offset surface
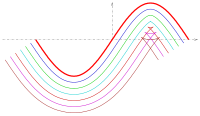
Imagine you have a clay pot with a smooth surface, which means the surface of the pot is not bumpy or lumpy. Now, let's say you want to make another pot that is slightly smaller than the original one. One way you can do this is by putting the original pot inside a bigger pot and adding clay around the outside of the original pot until it gets bigger. The new pot you made is called the "offset surface" because it is not the same size as the original pot, but it is still connected to it.
In computer graphics, an offset surface is the digital equivalent of adding clay around an object. In this case, the object is a digital model or shape that is represented by mathematical equations. To create an offset surface in computer graphics, the program takes the mathematical equation that defines the shape of the original object and creates a new, slightly larger or smaller shape around it. The distance between the original shape and the offset shape is called the "offset distance."
So, why would you want to create an offset surface in computer graphics? Well, for one thing, it can be useful for creating designs for things like product packaging, where you need to add space around the object to make room for labels or logos. It can also be used in engineering and manufacturing to create molds for objects like plastic parts or metal components.
So next time you see a shape with an offset surface, just remember it's like adding clay around an object to make it bigger or smaller. But this time, it's all digital and uses math equations to create the shape.
In computer graphics, an offset surface is the digital equivalent of adding clay around an object. In this case, the object is a digital model or shape that is represented by mathematical equations. To create an offset surface in computer graphics, the program takes the mathematical equation that defines the shape of the original object and creates a new, slightly larger or smaller shape around it. The distance between the original shape and the offset shape is called the "offset distance."
So, why would you want to create an offset surface in computer graphics? Well, for one thing, it can be useful for creating designs for things like product packaging, where you need to add space around the object to make room for labels or logos. It can also be used in engineering and manufacturing to create molds for objects like plastic parts or metal components.
So next time you see a shape with an offset surface, just remember it's like adding clay around an object to make it bigger or smaller. But this time, it's all digital and uses math equations to create the shape.
Related topics others have asked about:
