Pushforward (differential)
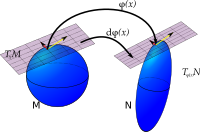
Imagine you have a toy car and you want it to move forward. You can do this by pushing it from the back. Similarly, in mathematics, the concept of pushforward refers to how a function affects the movement of objects in a space.
Let's say we have two spaces, A and B, and a function f that takes objects from A and maps them to objects in B. Now, suppose we have an object in A that we want to move to B. We can do this using the pushforward.
The pushforward is essentially the way the function f pushes the object from A to B. It tells us how the object will move under the influence of the function. It's like a set of instructions that tells us which way to go and how far to go.
To be more precise, the pushforward is a special type of function that takes vectors in A and maps them to vectors in B. It describes how the tangent space (which describes the direction and velocity of movement) of A is mapped to the tangent space of B under the effect of the function f.
In simpler terms, the pushforward tells us how a function affects the direction and magnitude of movement of an object in space.
So, just like pushing your toy car forward, a pushforward is a way of applying force to an object in one space to move it to another space. It allows us to understand how the object moves and changes as we apply various mathematical transformations to it.
Let's say we have two spaces, A and B, and a function f that takes objects from A and maps them to objects in B. Now, suppose we have an object in A that we want to move to B. We can do this using the pushforward.
The pushforward is essentially the way the function f pushes the object from A to B. It tells us how the object will move under the influence of the function. It's like a set of instructions that tells us which way to go and how far to go.
To be more precise, the pushforward is a special type of function that takes vectors in A and maps them to vectors in B. It describes how the tangent space (which describes the direction and velocity of movement) of A is mapped to the tangent space of B under the effect of the function f.
In simpler terms, the pushforward tells us how a function affects the direction and magnitude of movement of an object in space.
So, just like pushing your toy car forward, a pushforward is a way of applying force to an object in one space to move it to another space. It allows us to understand how the object moves and changes as we apply various mathematical transformations to it.
Related topics others have asked about:
