Reflection (mathematics)
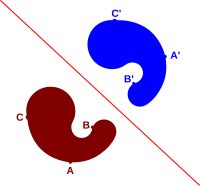
Reflection in mathematics is like looking at yourself in a mirror, but with shapes instead of your body. When you reflect a shape, you flip it over a line, and the new shape looks like a mirror image of the original shape. For example, if you draw a triangle on a piece of paper and reflect it over a line, the new triangle will look like a mirror image of the original one.
To reflect a shape, you need to choose a line called the line of reflection, which acts like the mirror. When you reflect a shape over a line of reflection, every point on the shape will be the same distance from the line of reflection as its reflected point is. This means that the distance between any point on the original shape and its corresponding point on the reflected shape will be the same as the distance between that point and the line of reflection.
Reflection is especially useful in geometry because it preserves some properties of a shape, such as angles and distances. This means that if you reflect a shape and then measure angles or distances, they will be the same as before the reflection. So, if you had a square and reflected it over a line, you would get another square that is the same size and has the same angles as the original square.
In summary, reflecting a shape in mathematics is like looking at it in a mirror. You choose a line of reflection, and then flip the shape over that line so that it looks like a mirror image of the original shape. This process preserves some important properties of the shape, like angles and distances.
To reflect a shape, you need to choose a line called the line of reflection, which acts like the mirror. When you reflect a shape over a line of reflection, every point on the shape will be the same distance from the line of reflection as its reflected point is. This means that the distance between any point on the original shape and its corresponding point on the reflected shape will be the same as the distance between that point and the line of reflection.
Reflection is especially useful in geometry because it preserves some properties of a shape, such as angles and distances. This means that if you reflect a shape and then measure angles or distances, they will be the same as before the reflection. So, if you had a square and reflected it over a line, you would get another square that is the same size and has the same angles as the original square.
In summary, reflecting a shape in mathematics is like looking at it in a mirror. You choose a line of reflection, and then flip the shape over that line so that it looks like a mirror image of the original shape. This process preserves some important properties of the shape, like angles and distances.
Related topics others have asked about:
