Shear stress
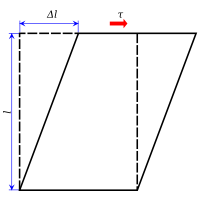
Shear stress is what happens when forces push or pull in opposite directions on something, like a piece of paper.
Imagine you have a piece of paper and you hold it at both ends with your hands. Now you move your hands in opposite directions, like you're trying to rip the paper apart. This creates shear stress on the paper because the top layer of fibers is being pulled in one direction and the bottom layer is being pushed in the other direction.
Shear stress happens in all kinds of materials, like liquids, gases, and even solids. When forces push or pull in different directions, it can cause the material to twist, bend, or break.
For example, when you walk on a slippery floor, your shoes slide across the surface. This creates shear stress between your shoes and the floor, which helps you move forward.
In the context of engineering and physics, understanding shear stress is really important because it can help us design and build things that can withstand different kinds of forces. Engineers use formulas and math to calculate shear stress in materials like steel, concrete, and aluminum, so that they can make sure buildings, bridges, and other structures are strong enough to support heavy loads and other stresses.
Imagine you have a piece of paper and you hold it at both ends with your hands. Now you move your hands in opposite directions, like you're trying to rip the paper apart. This creates shear stress on the paper because the top layer of fibers is being pulled in one direction and the bottom layer is being pushed in the other direction.
Shear stress happens in all kinds of materials, like liquids, gases, and even solids. When forces push or pull in different directions, it can cause the material to twist, bend, or break.
For example, when you walk on a slippery floor, your shoes slide across the surface. This creates shear stress between your shoes and the floor, which helps you move forward.
In the context of engineering and physics, understanding shear stress is really important because it can help us design and build things that can withstand different kinds of forces. Engineers use formulas and math to calculate shear stress in materials like steel, concrete, and aluminum, so that they can make sure buildings, bridges, and other structures are strong enough to support heavy loads and other stresses.
Related topics others have asked about:
