Sink (geography)
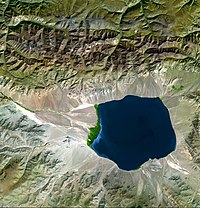
Imagine you have a bathtub with a hole in the bottom. When you fill the bathtub with water, the water will eventually drain out through the hole. Now let's imagine that the bottom of the bathtub isn't flat, but instead has a low spot where the water can get stuck. This low spot is like a sink in geography.
In geography, a sink is a place where water can get trapped in a low spot in the land. It can happen naturally, like with a sinkhole, which is a hole in the ground that forms when the earth collapses. It can also happen when water collects in a basin-like area or depression in the ground.
Sinks are part of the water cycle, which is the way that water moves around the earth. When it rains, water collects in sinks and other low areas. This is called "surface water." Some of the water in the sink will soak into the ground, while some of it will evaporate into the air. The water that soaks into the ground is then stored in layers of rock and soil, which is called "groundwater."
Sinks can also have other important functions. For example, a sink can provide a habitat for plants and animals that need water to survive. It can also be an important source of water for people, especially in areas where there isn't a lot of rain.
So in summary, a sink in geography is a low spot in the land where water can collect and soak into the ground or evaporate into the air. It plays an important role in the water cycle and can also be important for plants, animals, and people.
In geography, a sink is a place where water can get trapped in a low spot in the land. It can happen naturally, like with a sinkhole, which is a hole in the ground that forms when the earth collapses. It can also happen when water collects in a basin-like area or depression in the ground.
Sinks are part of the water cycle, which is the way that water moves around the earth. When it rains, water collects in sinks and other low areas. This is called "surface water." Some of the water in the sink will soak into the ground, while some of it will evaporate into the air. The water that soaks into the ground is then stored in layers of rock and soil, which is called "groundwater."
Sinks can also have other important functions. For example, a sink can provide a habitat for plants and animals that need water to survive. It can also be an important source of water for people, especially in areas where there isn't a lot of rain.
So in summary, a sink in geography is a low spot in the land where water can collect and soak into the ground or evaporate into the air. It plays an important role in the water cycle and can also be important for plants, animals, and people.
Related topics others have asked about:
