Standard electrode potential
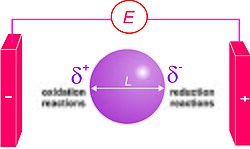
Okay kiddo, so let me explain to you what a standard electrode potential means. Imagine you have two different metals, one is copper and the other is silver. Now imagine you put these two metals in a solution called an electrolyte. When you do this, the metals start to react with the electrolyte, and we see some changes.
Now, let me tell you that each metal has its own tendency to lose or gain electrons when it's placed in an electrolyte. This tendency is called an electrode potential, which we measure in volts. When we measure this potential under standard conditions (i.e., when the temperature, pressure, and concentration of the electrolyte are all standard), we call it the standard electrode potential.
Now with copper and silver, if you measure their electrode potentials in the same electrolyte, you can compare them and see which metal has a greater tendency to lose or gain electrons. If silver has a higher tendency to lose electrons, we say it has a higher standard electrode potential compared to copper, which has a lower tendency to lose electrons.
This standard electrode potential can help us predict whether a chemical reaction will occur or not in a given situation. If we know the standard electrode potential, we can calculate the overall potential or energy release of the reaction.
Overall, the standard electrode potential helps us understand the behavior of different elements in a solution and how they react with each other. Does that help, kiddo?
Now, let me tell you that each metal has its own tendency to lose or gain electrons when it's placed in an electrolyte. This tendency is called an electrode potential, which we measure in volts. When we measure this potential under standard conditions (i.e., when the temperature, pressure, and concentration of the electrolyte are all standard), we call it the standard electrode potential.
Now with copper and silver, if you measure their electrode potentials in the same electrolyte, you can compare them and see which metal has a greater tendency to lose or gain electrons. If silver has a higher tendency to lose electrons, we say it has a higher standard electrode potential compared to copper, which has a lower tendency to lose electrons.
This standard electrode potential can help us predict whether a chemical reaction will occur or not in a given situation. If we know the standard electrode potential, we can calculate the overall potential or energy release of the reaction.
Overall, the standard electrode potential helps us understand the behavior of different elements in a solution and how they react with each other. Does that help, kiddo?
Related topics others have asked about:
