Voice onset time
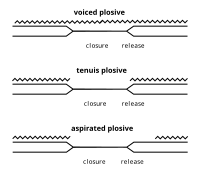
Voice onset time (VOT) is a fancy word used to describe the time difference between when you open your mouth to make a sound and when your vocal cords start vibrating to make that sound. Let's say you want to say the word "ball". Before you say "buh", your mouth needs to open and get ready to make the sound. Then, after a tiny bit of time, your vocal cords start vibrating, making the "buh" sound you hear. The time between when your mouth opens and your vocal cords start vibrating is called the VOT.
VOT is important because it can change the meaning of a word. For example, the word "bat" with a short VOT means something different than the word "pat" with a longer VOT. When you say "bat", your mouth opens and your vocal cords start vibrating almost at the same time, making the abrupt "b" sound. But when you say "pat", you open your mouth first, then wait a tiny bit longer before your vocal cords vibrate to make the "puh" sound.
Researchers can measure VOT using special equipment that records the sound you make when you speak. They study VOT to understand how different sounds are made in different languages and how our brains process and understand speech.
VOT is important because it can change the meaning of a word. For example, the word "bat" with a short VOT means something different than the word "pat" with a longer VOT. When you say "bat", your mouth opens and your vocal cords start vibrating almost at the same time, making the abrupt "b" sound. But when you say "pat", you open your mouth first, then wait a tiny bit longer before your vocal cords vibrate to make the "puh" sound.
Researchers can measure VOT using special equipment that records the sound you make when you speak. They study VOT to understand how different sounds are made in different languages and how our brains process and understand speech.
