Alkaline precipitation
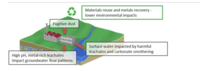
Alkaline precipitation is the process of separating minerals and impurities from water or other solutions by adding a special type of chemical called an alkaline agent (like baking soda or ammonia) to make it more basic, or alkaline.
Think of it like making a cake, where you add baking soda to make the batter rise and become fluffy. In the same way, when we add an alkaline agent to a solution that contains some minerals or impurities, it reacts with them and causes them to form solid particles.
These solid particles can then be easily removed from the solution by filtering, settling or centrifugation methods, leaving behind a cleaner and purer form of liquid.
Alkaline precipitation is often used to purify water from various sources like rivers, lakes or underground wells, to remove harmful metals like lead, mercury or cadmium, and to treat wastewater before it's released back into the environment.
Think of it like making a cake, where you add baking soda to make the batter rise and become fluffy. In the same way, when we add an alkaline agent to a solution that contains some minerals or impurities, it reacts with them and causes them to form solid particles.
These solid particles can then be easily removed from the solution by filtering, settling or centrifugation methods, leaving behind a cleaner and purer form of liquid.
Alkaline precipitation is often used to purify water from various sources like rivers, lakes or underground wells, to remove harmful metals like lead, mercury or cadmium, and to treat wastewater before it's released back into the environment.
Related topics others have asked about:
