Animal echolocation
Have you ever heard a bat or a dolphin making strange sounds? They use a special power called echolocation to make sense of the world around them. Imagine if you were blindfolded and had to figure out what was in a room without using your eyes. You might use your hands to feel around for objects, but animals with echolocation use sound instead of touch.
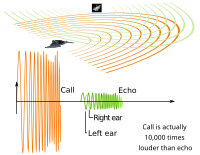
Echolocation works by sending out high-pitched sounds, or clicks, that bounce off of objects and come back as echoes. The animal then listens to the echoes to understand its surroundings. The echoes tell the animal how far away an object is, how big it is, and even what shape it is.
For example, when a bat sends out a high-pitched sound, it will bounce off of a bug and return as an echo. The bat can then use the echo to locate the bug, fly to it, and eat it. This helps the bat hunt for food even in complete darkness.
Dolphins use echolocation to find their way through the ocean and to locate prey. They can even distinguish between different types of fish based on the echoes they receive.
Other animals that use echolocation include whales, shrews, and some birds. It’s an amazing superpower that helps these animals survive and thrive in their environments.
Echolocation works by sending out high-pitched sounds, or clicks, that bounce off of objects and come back as echoes. The animal then listens to the echoes to understand its surroundings. The echoes tell the animal how far away an object is, how big it is, and even what shape it is.
For example, when a bat sends out a high-pitched sound, it will bounce off of a bug and return as an echo. The bat can then use the echo to locate the bug, fly to it, and eat it. This helps the bat hunt for food even in complete darkness.
Dolphins use echolocation to find their way through the ocean and to locate prey. They can even distinguish between different types of fish based on the echoes they receive.
Other animals that use echolocation include whales, shrews, and some birds. It’s an amazing superpower that helps these animals survive and thrive in their environments.
Related topics others have asked about:
