Crossbar switch
Imagine you have a toy box with lots of toys inside. You want to share your toys with your friends who are coming to play with you, but you only have one toy to give away at a time. To solve this problem, you came up with a plan. You divided all your toys into different groups, and you made a list of your friends who are coming to play with you. You put a label on each group of toys with the name of the friend who would like to play with them. Then you wrote down which toy you gave to which friend, so you wouldn't forget. This way, whenever your friends arrived, you would know which toy to give to which friend.
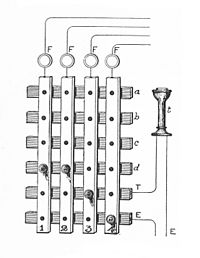
A crossbar switch works similarly to your toy box, but instead of toys and friends, it connects devices in a computer or a telecommunication system. A crossbar switch is like a traffic controller that directs signals from one device to another. It is called a crossbar switch because it uses a matrix of crossed wires to connect different devices together.
In a crossbar switch, there are input and output wires that carry signals from devices such as phones, computers, or cameras. Whenever there is a signal that needs to go to a specific output device, the switch uses a matrix of crossed wires to connect the input wire to the output wire that leads to the desired device. This means that the signals are switched or redirected from one input to one or more outputs based on the routing rules.
The matrix of crossed wires in a crossbar switch creates a set of logical paths that connect all input and output devices together. These paths are organized and controlled by a central unit called the controller, which determines which signals are forwarded to which devices based on their addresses.
Overall, a crossbar switch is a powerful communication tool that allows multiple devices to share resources and communicate with each other efficiently. It is like a traffic controller that makes sure everyone gets where they need to be without getting stuck in traffic jams.
A crossbar switch works similarly to your toy box, but instead of toys and friends, it connects devices in a computer or a telecommunication system. A crossbar switch is like a traffic controller that directs signals from one device to another. It is called a crossbar switch because it uses a matrix of crossed wires to connect different devices together.
In a crossbar switch, there are input and output wires that carry signals from devices such as phones, computers, or cameras. Whenever there is a signal that needs to go to a specific output device, the switch uses a matrix of crossed wires to connect the input wire to the output wire that leads to the desired device. This means that the signals are switched or redirected from one input to one or more outputs based on the routing rules.
The matrix of crossed wires in a crossbar switch creates a set of logical paths that connect all input and output devices together. These paths are organized and controlled by a central unit called the controller, which determines which signals are forwarded to which devices based on their addresses.
Overall, a crossbar switch is a powerful communication tool that allows multiple devices to share resources and communicate with each other efficiently. It is like a traffic controller that makes sure everyone gets where they need to be without getting stuck in traffic jams.
Related topics others have asked about:
