Eisenstein integer
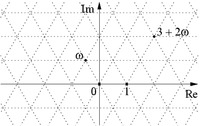
An Eisenstein integer is a special kind of number that you can use to help solve certain math problems. It looks a bit different than the numbers we usually use because it has three parts: a real part (like 1 or 2), and two imaginary parts (like i and j in regular imaginary numbers).
Think of a piece of paper with a coordinate grid, and you know how to find points like (2, 3) or (-1, -5) on the grid. Eisenstein integers also live on a coordinate grid, but instead of just having an x-axis and a y-axis, they have two different imaginary axes, which we call j and omega.
So if we want to find the Eisenstein integer at the point (2, 3) on this grid, we write it as 2 + 3j. And if we want to find the Eisenstein integer at (-1, 4) on the same grid, we write it as -1 + 4j.
Eisenstein integers are cool because they have some interesting properties when you multiply or divide them. They're also related to some other areas of math, like geometry and number theory, which makes them useful in a lot of different contexts.
Think of a piece of paper with a coordinate grid, and you know how to find points like (2, 3) or (-1, -5) on the grid. Eisenstein integers also live on a coordinate grid, but instead of just having an x-axis and a y-axis, they have two different imaginary axes, which we call j and omega.
So if we want to find the Eisenstein integer at the point (2, 3) on this grid, we write it as 2 + 3j. And if we want to find the Eisenstein integer at (-1, 4) on the same grid, we write it as -1 + 4j.
Eisenstein integers are cool because they have some interesting properties when you multiply or divide them. They're also related to some other areas of math, like geometry and number theory, which makes them useful in a lot of different contexts.
Related topics others have asked about:
