Galvanic cell
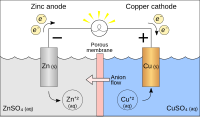
A galvanic cell is a way to make electricity. It uses chemicals that react with each other to make electric current. The main parts of a galvanic cell are two different kinds of metal (for example copper and zinc). The two metals are put into a solution made of water and other chemicals.
When the two metals are in the solution, they react with each other in a special way. One of the metals absorbs electrons from the other metal, and this causes the electrons to flow. This electron flow creates electric current that can power things like a light bulb.
When the two metals are in the solution, they react with each other in a special way. One of the metals absorbs electrons from the other metal, and this causes the electrons to flow. This electron flow creates electric current that can power things like a light bulb.
Related topics others have asked about:
