Ideal gas law
Okay kiddo, so have you ever seen a balloon filled with air? Imagine it's a really big balloon that can expand or shrink based on how much air you put in it.
Now the air we put in the balloon is made up of tiny things called molecules. These molecules are bouncing around inside the balloon and they push against the walls of the balloon.
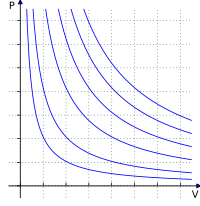
The ideal gas law is like a formula that helps us understand how these molecules behave. It tells us that the pressure (that's the pushing force of the air molecules) inside the balloon is related to how many air molecules are in there, how much space the balloon has, and how fast the molecules are moving around.
So, let's say we have a big balloon that's really full of air. The air molecules are bouncing around like crazy and pushing hard against the walls of the balloon. This creates a lot of pressure inside the balloon. But, if we let some of the air out of the balloon, there would be fewer molecules bouncing around and pushing against the walls. This means the pressure would go down.
That's basically what the ideal gas law helps us figure out - how the pressure, number of molecules, volume of space, and temperature of gas all relate to each other. So, with this knowledge, scientists can predict what will happen to gases under different conditions and make really cool things like rockets and balloons!
Now the air we put in the balloon is made up of tiny things called molecules. These molecules are bouncing around inside the balloon and they push against the walls of the balloon.
The ideal gas law is like a formula that helps us understand how these molecules behave. It tells us that the pressure (that's the pushing force of the air molecules) inside the balloon is related to how many air molecules are in there, how much space the balloon has, and how fast the molecules are moving around.
So, let's say we have a big balloon that's really full of air. The air molecules are bouncing around like crazy and pushing hard against the walls of the balloon. This creates a lot of pressure inside the balloon. But, if we let some of the air out of the balloon, there would be fewer molecules bouncing around and pushing against the walls. This means the pressure would go down.
That's basically what the ideal gas law helps us figure out - how the pressure, number of molecules, volume of space, and temperature of gas all relate to each other. So, with this knowledge, scientists can predict what will happen to gases under different conditions and make really cool things like rockets and balloons!
Related topics others have asked about:
