Loxodromic navigation
Have you ever wondered how a plane, ship or even a bird can go from one point to another in the shortest possible distance? Well, that's what loxodromic navigation is all about.
Imagine you and your friend want to walk from your home to a park that is far away. If you walk straight towards the park, it may take you a very long time to get there because there may be obstacles like buildings or traffic that you have to avoid. So, instead of walking straight towards the park like a line, you could draw a line that curves slightly towards the park. This line is called a loxodrome.
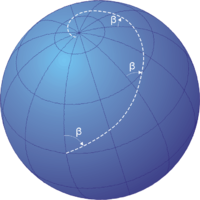
A loxodrome is a line on a globe or a map that crosses all meridians (imaginary lines that run from the North to the South Pole) at the same angle. This angle is called the rhumb line, and it's important because it means that you can follow a straight line without changing direction too much, making it easier to navigate.
Now, let's say you're in a plane flying from New York to London. You could follow a loxodrome that goes across the Atlantic Ocean, and you wouldn't have to keep changing direction all the time because the loxodrome keeps you on the same course. You could even use a compass to help you follow the rhumb line.
Loxodromic navigation is not just for airplanes and ships. Birds also use a kind of loxodromic navigation known as vector navigation. Birds use visual landmarks like mountains, coastlines, or stars to follow a loxodrome on their way to their destination.
So, loxodromic navigation is all about finding the shortest distance between two points while keeping a constant direction. It's a clever way of getting from one place to another without getting lost!
Imagine you and your friend want to walk from your home to a park that is far away. If you walk straight towards the park, it may take you a very long time to get there because there may be obstacles like buildings or traffic that you have to avoid. So, instead of walking straight towards the park like a line, you could draw a line that curves slightly towards the park. This line is called a loxodrome.
A loxodrome is a line on a globe or a map that crosses all meridians (imaginary lines that run from the North to the South Pole) at the same angle. This angle is called the rhumb line, and it's important because it means that you can follow a straight line without changing direction too much, making it easier to navigate.
Now, let's say you're in a plane flying from New York to London. You could follow a loxodrome that goes across the Atlantic Ocean, and you wouldn't have to keep changing direction all the time because the loxodrome keeps you on the same course. You could even use a compass to help you follow the rhumb line.
Loxodromic navigation is not just for airplanes and ships. Birds also use a kind of loxodromic navigation known as vector navigation. Birds use visual landmarks like mountains, coastlines, or stars to follow a loxodrome on their way to their destination.
So, loxodromic navigation is all about finding the shortest distance between two points while keeping a constant direction. It's a clever way of getting from one place to another without getting lost!
Related topics others have asked about:
