Sensor node
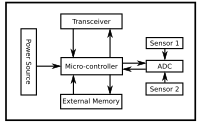
A sensor node is like a little detective that helps us understand what's going on around us. It's made up of three important parts: a sensor, a microcontroller, and a wireless transmitter.
The sensor is like a little eye or ear that can measure things like temperature, humidity, light, movement, or sound. For example, a temperature sensor can tell us if it's too hot or too cold.
The microcontroller is like the brain of the sensor node. It processes the information that the sensor collects and decides what to do next.
The wireless transmitter helps the sensor node communicate with other devices, like a computer or a phone.
To understand how a sensor node works, imagine you're playing a game of tag with your friends. You want to know where all your friends are so you can tag them. You put on a special bracelet that has a sensor node.
The sensor node can measure how far away your friends are, and the microcontroller can use that information to figure out where they are. It can also use the wireless transmitter to send that information to a computer or a phone.
Now, you can use that information to tag your friends and win the game!
In summary, a sensor node is like a little detective that can measure things and send that information to other devices. It has a sensor, a microcontroller, and a wireless transmitter, and it helps us understand the world around us.
The sensor is like a little eye or ear that can measure things like temperature, humidity, light, movement, or sound. For example, a temperature sensor can tell us if it's too hot or too cold.
The microcontroller is like the brain of the sensor node. It processes the information that the sensor collects and decides what to do next.
The wireless transmitter helps the sensor node communicate with other devices, like a computer or a phone.
To understand how a sensor node works, imagine you're playing a game of tag with your friends. You want to know where all your friends are so you can tag them. You put on a special bracelet that has a sensor node.
The sensor node can measure how far away your friends are, and the microcontroller can use that information to figure out where they are. It can also use the wireless transmitter to send that information to a computer or a phone.
Now, you can use that information to tag your friends and win the game!
In summary, a sensor node is like a little detective that can measure things and send that information to other devices. It has a sensor, a microcontroller, and a wireless transmitter, and it helps us understand the world around us.
Related topics others have asked about:
